我们可以通过分析经典的系统, 理解分布式系统设计. 比如, Frangipani, Dynamo, Memcache, Redis Cluster, Spanner. 这些系统在Paper Trail, MIT Distributed System中都有分析和介绍, 系统的论文也可以在阅读清单中找到. 本文试图把这些系统放在一起, 对比各自不同的需求场景, 理解系统作者背后的选择权衡, 从而在面对现实的分布式问题中, 做出更好的选择.
1 Frangipani. Serializable FileSystem
Frangipani是一个分布式的文件系统(1997), 为了实现多人在线编辑文件的场景. 在简化使用场景下, Frangipani不支持多人同时在线编辑同一个文件, 即独占式的写入.
在这个场景下, 需要满足两方面的需求:
1) 每个workstation(WS)写的数据不能丢, 数据不能相互覆盖, 同时不存在写后读不到的逻辑问题. 2) workstation的读写性能很好, 就像在本地编写一样.
设计分析:
- 低延时. 因此需要在workstation缓存一份数据, 在本地修改数据, 再提交.
- 强一致性. WS读写独占, 相当于是串行化的隔离级别(Serializable), 通过一个Lock Server, 操作前加锁, 操作完成后释放锁.
可见, Frangipani需要一个cache coherence protocol, 详细过程如下:
Frangipani's coherence protocol (simplified):
lock server (LS), with one lock per file/directory
file owner
-----------
x WS1
y WS1
workstation (WS) Frangipani cache:
file/dir lock content
-----------------------
x busy ...
y idle ...
if WS holds lock,
busy: using data right now
idle: holds lock but not using the cached data right now
workstation rules:
don't cache unless you hold the lock
acquire lock, then read from Petal(storage system)
write to Petal, then release lock
coherence protocol messages:
request (WS -> LS)
grant (LS -> WS)
revoke (LS -> WS)
release (WS -> LS)
一个完整的获取锁的过程, 当WS1想要读或者写时, 先向LS reqeust lock. LS 如果对应的文件没有加锁, 标记文件为占有状态, 所有者为WS1. 否则向锁的所有者WS2 grant锁, 等待WS2 写完成, 释放锁. WS1 被LS revoke.
占有状态分为busy和idle状态, 区分WS的读和写. idle状态(只读)的锁, 不存在写一致性问题, 可以直接抢占锁.
总结:
Frangipani是一个典型的CP系统, 牺牲可用性, 达到系统的强一致性和缓存的分区. 通过一个Lock Server节点, 实现各个节点对资源的顺序读写, 达到整体的强一致性.
2 Dynamo 去中心化高可用的KV存储
Dynamo是Amazon设计的去中心化的高可用的Key-Value存储. 最初被用来构建购物车应用, 后面延续到其他的应用场景, 在Amazon的业务场景下, 一个存储系统需要:
- 大规模, 可靠性. 支持Tens of thousands of servers and network components, 在这个量级下设备和环境的问题被放大, 作为基础设施需要兼容异常, 简化上层业务.
- 扩展性, highly scalable to support continuous growth. 易于扩展.
- 主键存储. 简化的数据模型, 只支持主key模式的数据存储. 降低RDB带来的额外开销.
- 高性能, 低延迟. 满足购物车查询和修改的延迟要求.
为了满足实际需求, 需要解决扩展性, 高可用, 异常处理和异常检测的问题, 问题和方法如下(来自Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store )
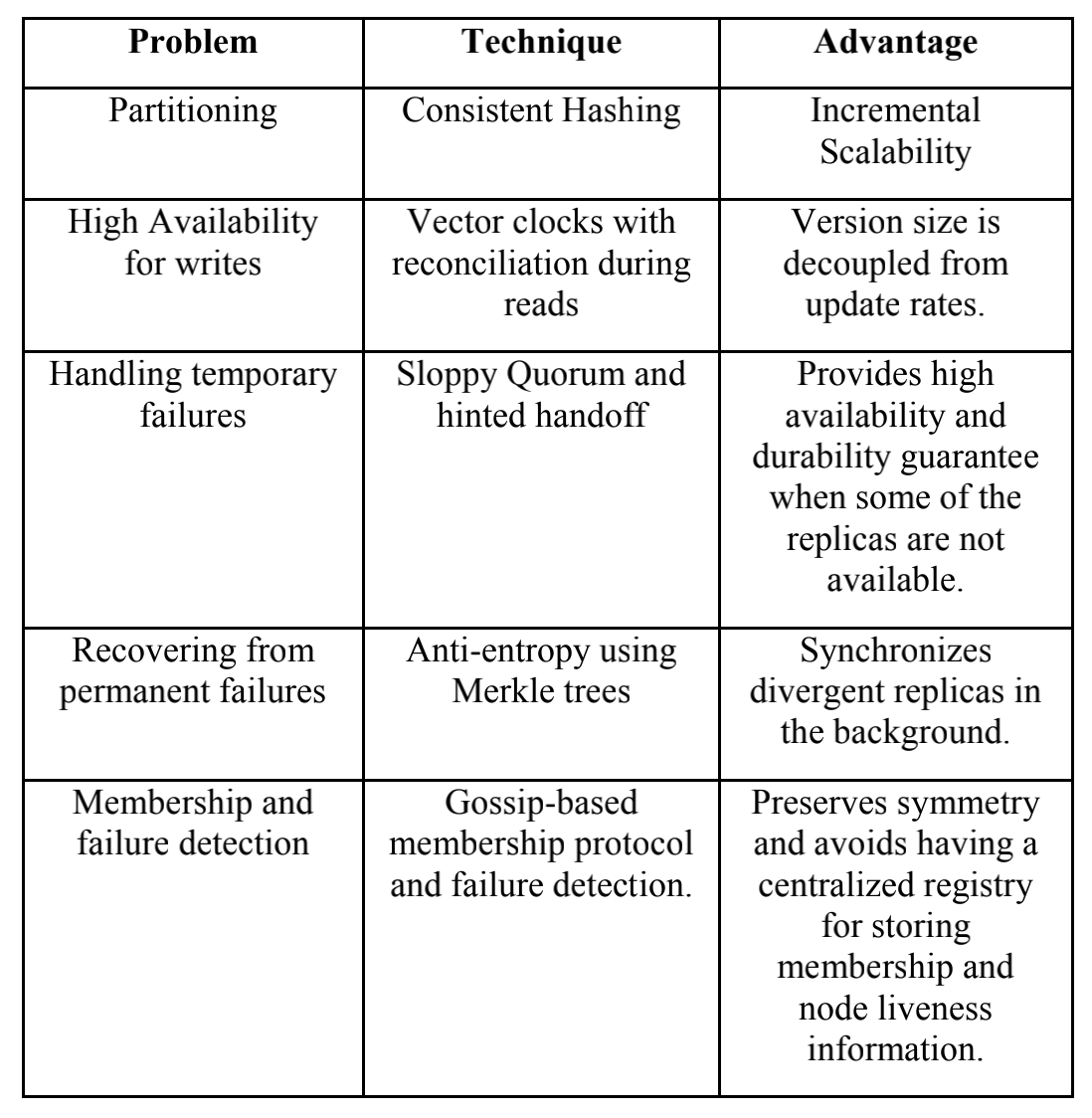
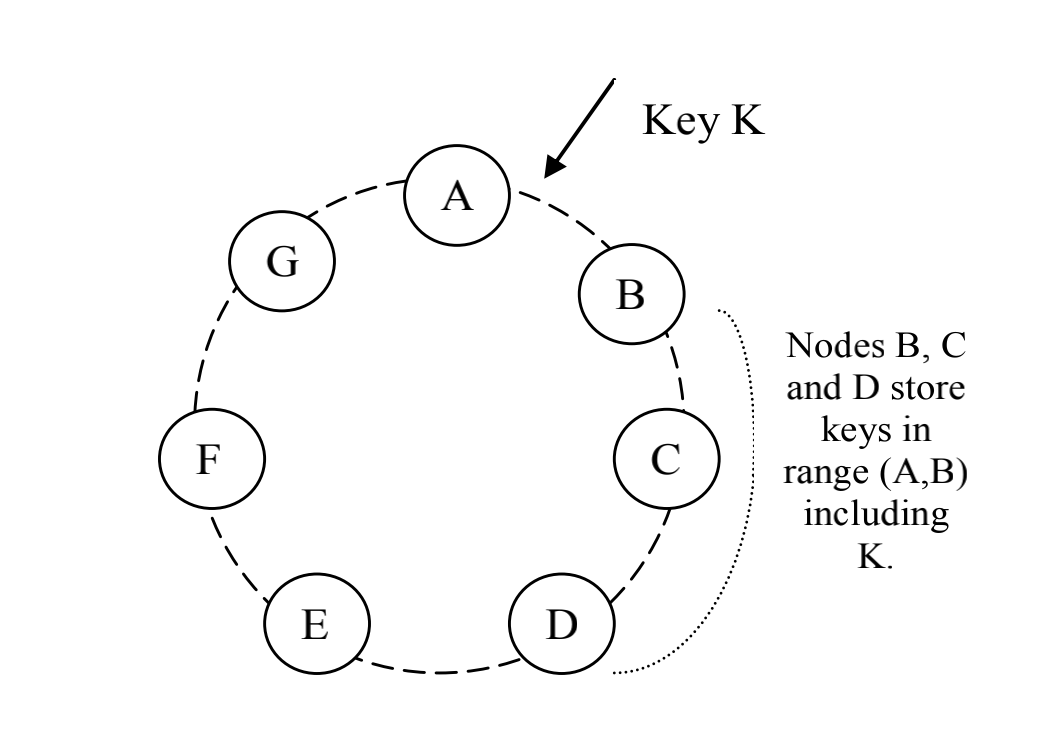
在扩展性上(Partition), 常用的方法是对key做垂直拆分, 使得数据分散到不同的节点上. 拆分的方法, 一种是将查询主键均匀的分散到固定数量的节点上, 手动分配和管理拆分关系的好处是简单和均匀, 缺点是扩展性差, 节点异常处理困难(通常配合Master-Slave或Load Balance做高可用); 另一种方式, 使用一致性Hash, 将key的读写随机分散到各个节点上. 好处是扩展方便, 新增节点只需要相邻节点做数据迁移, 同时降低扩展的运维成本. 缺点是节点随机分配hash空间, 分配不均匀(通过增加vnode节点, 和自适应的调节节点Hash值调节).
高可用(Available)方面, 数据会replicate到N个节点上(按照Hash环的顺序分配节点), 读, 写会同时操作W和R个节点(W+R>N, N通常=3), 保障数据不丢. 使用Vector Clock这样一个Conflict Free的结构避免了请求锁, 在网络分区发生脑裂时, 可以同时保存多个版本的数据, 在网络恢复时可以尝试合并版本或把多版本返回给调用方, 由调用方解决冲突.
因此, Dynamo通过保持一个quorum-like的技术, 使用多版本的结构, 通过降低一致性, 提升系统高可用.
异常处理方面, 使用Sloppy Quorum和Hinted handoff提升可用性. 即当节点A异常时, 后续的节点D会暂时代替异常节点接收写请求, 并把临时的写入单独记录(separate local database), 当节点A恢复时, D会将数据和请求交给A, 当数据转移成功后, 临时数据会被删除.
在异常检测方面, 使用了Merkle tree来高效的对比数据的差异.
A Merkle tree is a hash tree where leaves are hashes of the values of individual keys. Parent nodes higher in the tree are hashes of their respective children.
The principal advantage of Merkle tree is that each branch of the tree can be checked independently without requiring nodes to download the entire tree or the entire data set. Moreover, Merkle trees help in reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred while checking for inconsistencies among replicas.
节点之间使用Gossip协议检测异常和同步状态, 每个节点都对等的保存所有节点的metadata, 整个系统是完全去中心化的.
一个完整的写入和读取的过程如下:
Put:
find first node of preference list as the coordinator
coordinator generates vector lock and write locally
write to buffer first
writer thread periodically sync to disk
send to N highest-ranked node
if at least W-1 respond, success
else failed
Get:
find first node of preference list as the coordinator
send to N highest-ranked node
waits for R responses before returning the result to the client.
read from buffer first,
then from the disk.
if all version are the same, success
else returns all the versions it deems to be causally unrelated
The divergent versions are then reconciled and the reconciled version superseding the current versions is written back.
其中, 为了简化服务节点, 所有的put和get都是由客户端向服务端发起的. 使用了buffer write等技术提升写入的Thoughout.
总结
在2012年, Dynamo创造性的组合了各种分布式技术, 解决了Amazon的扩展性和高可用问题. 为我们设计分布式架构提供了非常多好的思路.
但是根据Werner的描述, Dynamo在Amazon内部没有推广使用. 尽管Dynamo的设计很精妙, 但操作运维的复杂度(Operational Complexity)和系统规模带来的理解成本, 让大多数技术人员望而却步. 至今很多关键的商业数据存储, 还是使用最简单可靠的主从复制+垂直拆分方案.
“Developers strongly preferred simplicity to fine-grained control, they voted with their feet and adopted cloud-based AWS solutions, like Amazon S3 and Amazon SimpleDB, over Dynamo”.
后续在数据结构和Cloud Base方向演进, 经过多年的演进, 系统越来越成熟, 变成了现在的DynamoDB.
3 Reference
Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store