1 Memcache 分布式HashTable缓存 (DHT)
Memcache是Facebook在单机版memcached基础上设计的分布式的KV存储. 在Facebook, 对分布式HashTable(DHT)的使用需求:
1) near real-time communication.
2) aggregate content on-the-fly from multi sources
3) able to access and update popular shared content
4) scale to millions qps.
5) Read-heavy workload and wide fan-out.
Memcache用做数据的缓存, 在设计上有取舍, 降低整体系统的复杂性:
1) 按需的lool-aside cache. Choose to delete cache data instead of update, cause of idempotent.
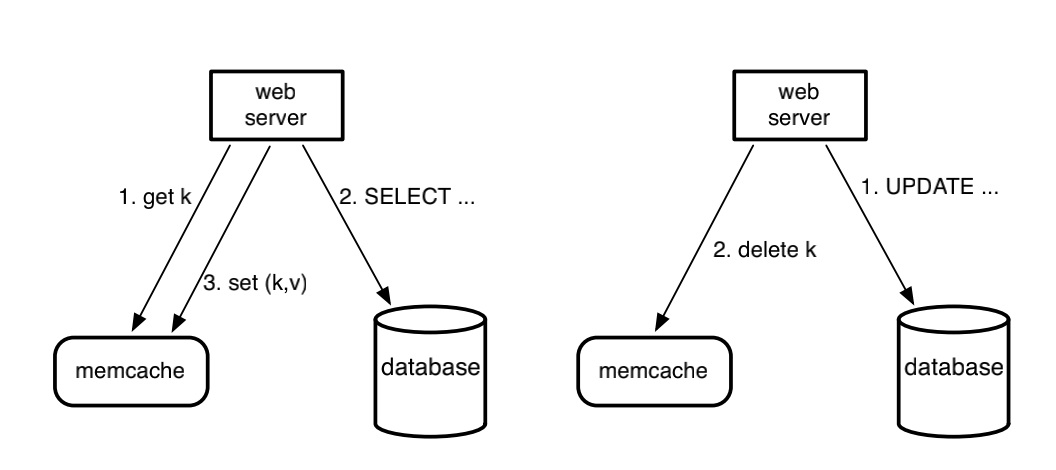
look-aside cache的流程如下, 读取时, 先读缓存再读db, cacahe miss写缓存. 更新时, 先写db, 再失效缓存. 失效缓存而不是更新缓存, 避免了concurrent更新缓存带来的时序问题(由db解决).
2) 各个Memcache服务之间不做通信, 各个Region之间通过数据库做同步. 数据一致性由后端存储(MySQL)保障. (最终一致性). 保持memcache 是stateless的server. 各个实例独立运行, Memcache很容易水平扩展, 增加服务, 不影响现有的节点. 但不能直接做数据的Partition(依赖DB的Partition).
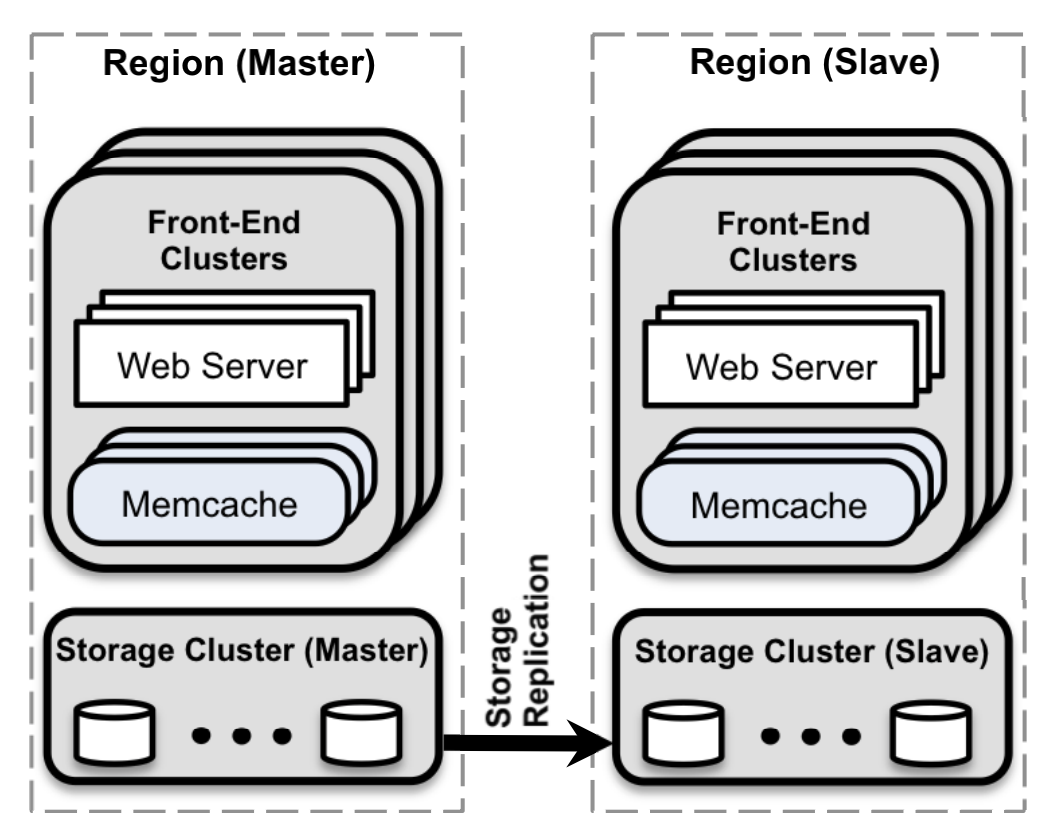
此外, Memcache在系统延迟, 异常处理, 缓存冷启, 跨Region一致性优化上, 有很多实践的经验.
- 降低系统延迟:
1) 使用batch和并发请求. 通过DAG(DAG represent dependcy of data.)一次获取多个key的数据. Client-Server之间也通过并发请求降低延迟.
2) Client-Server通信优化. 读取请求(get)使用udp降低延迟和负载. put/delete请求使用tcp保证可靠性. 实践经验udp network failure 0.25% (80% late or drop packet), 将网络异常treat as error, 但skip fill memcached, 避免不必要的网络开销.
3) Incast congestion: 使用sliding window限制incast congestion. 发生Incast congestion的原因是, client会并发请求大量的key, response有可能同时到达, 从而把路由器等设备打卦.
- 使用租约(lease)降低后端负载:
-
当cache miss的时候会生成lease. lease is a 64-bit token bound to the specific key the client originally requested.
-
stale write: happens when concurrent update to memcache get reordered. 当set value时, 会校验lease.如果key在request到put期间收到了delete reqeust, lease会失效.
考虑以下场景R1, R2先后两次读取, U1, U2先后两次更新, 分别更新值为A,B, 更新都先于读. 因此R1,R2触发了两次写W1,W2. 如果W2先于W1到达, 则最终值为A. 即为stale write.
带lease的场景, W2由R2触发, lease有效可以更新. W1由R1触发, lease期间有数据更新U2, 因此lease失效, 更新被拒绝. 因此最终值为B.
-
缓存击穿(thundering herds): token每10秒会生成一个, 在10秒内, client带有lease的请求会被延迟hold一段时间, 这样当请求时, 缓存的数据已经被更新. 从而减少了大量的数据更新时带来的缓存击穿问题.
- Handle failures:
Dedicate a small set of machines(1%), to take over the responsiblities of a few failed servers, named Gutter.
When a memcached client receives no response to its get request, the client assumes the server has failed and issues the request again to the Gutter pool.
Regional Invalidation: MySQL commit log - batch deletes to McSqueal - unpack to individual memcache server
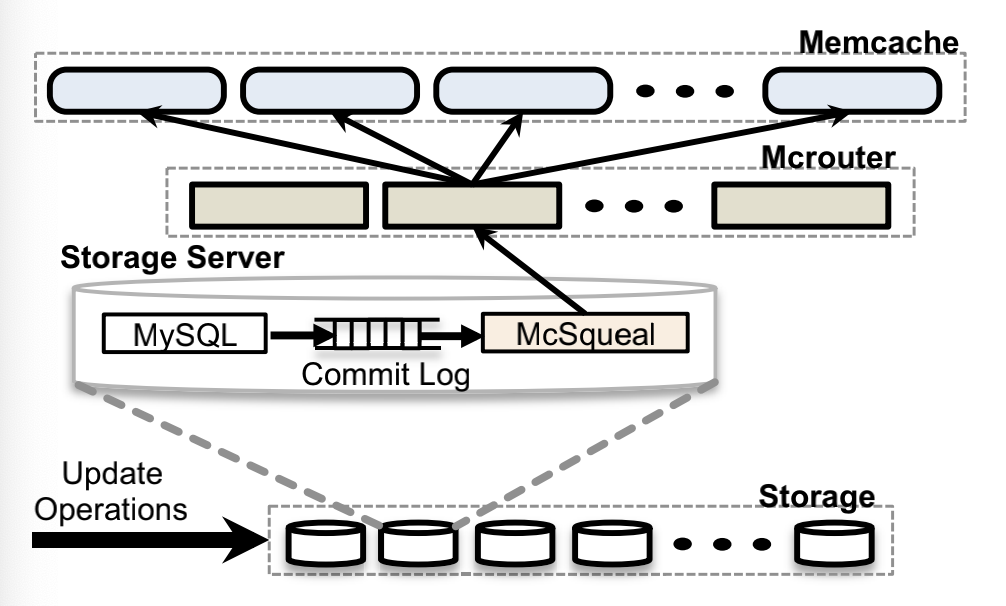
- Cold Cluster Warmup: Allow “cold cluster” retrieve data from “warm cluster” rather than a persitent storage.
Race conditions: cold cluster database update - simultaneously request stale data from warm cluster.
solution:
Client:
when a miss id detected,
client re-request the key from the warm cluster
and adds it into the cold cluster.
Cold Cluster: all deletes to colud cluster issued with a two second hold-off (which reject add)
the failure of add indicates that the newer data is avaliable.
client refetch on the database.
Close time: When cold cluster’s hit rate stabilizse.
- Across Region Consistency:
Benifits: local memcached server + local MySql provides low latency; avoids reace condition in which an invalidation arrives before the data replicated from the master db region.
Problem: replica may lag behind the master database. reqeust may get the stale data be
Solution: provide best-effort eventual consistency. Use remote marker to minimize the probability of reading stale data. the marker indicates that data in the local replica database are potentially stale, and the query should be redirected to the master region.
1) befrore client update key k, set a remote marker in the region
2) client perform write to the master db.
3) client deletes k in the local memcache cluster.
4) client get cache miss, check the remote marker of k, decide whether direct query to master/local databese.
Trade consistency with speed.
2 Redis
- Availability master replica pattern support async(default) and sync replication.
replica PSYNC -> master <Replication ID, offset> 查询backlog 计算incremental update or 查询不到 full sync background process RDB file buffer commands load RDB file, send all to replica
A replication ID basically marks a given history of the data set. Every time an instance restarts from scratch as a master, or a replica is promoted to master, a new replication ID is generated for this instance.
why a replica promoted to master needs to change its replication ID after a failover: it is possible that the old master is still working as a master because of some network partition: retaining the same replication ID would violate the fact that the same ID and same offset of any two random instances mean they have the same data set.
Redis Cluster
Hash Slot:
Every node is connected to every other node, The client is in theory free to send requests to all the nodes in the cluster, getting redirected if needed.
https://medium.com/opstree-technology/redis-cluster-architecture-replication-sharding-and-failover-86871e783ac0#:~:text=Redis%20Cluster%20is%20an%20active,a%20subset%20of%20those%20slots https://redis.io/docs/manual/replication/
-
Consistency https://www.allthingsdistributed.com/2021/11/amazon-memorydb-for-redis-speed-consistency.html
Redis Cluster uses asynchronous replication between nodes, and last failover wins implicit merge function. This means that the last elected master dataset eventually replaces all the other replicas. There is always a window of time when it is possible to lose writes during partitions.
防止split brain: 奇数个master, 每个master两个replica.
-
Persistence https://redis.io/docs/manual/persistence/
-
Performance – IO MultiPlexing - epoll/kqueue Redis event library https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/99ab4236afb210dc118fad892210b9fbb369aa8e/src/ae.c https://austingwalters.com/io-multiplexing/
– Single Thread
– Pipelining https://redis.io/docs/manual/pipelining/#:~:text=Redis%20is%20a%20TCP%20server,way%2C%20for%20the%20server%20response.
https://aws.amazon.com/redis/
3 Spanner
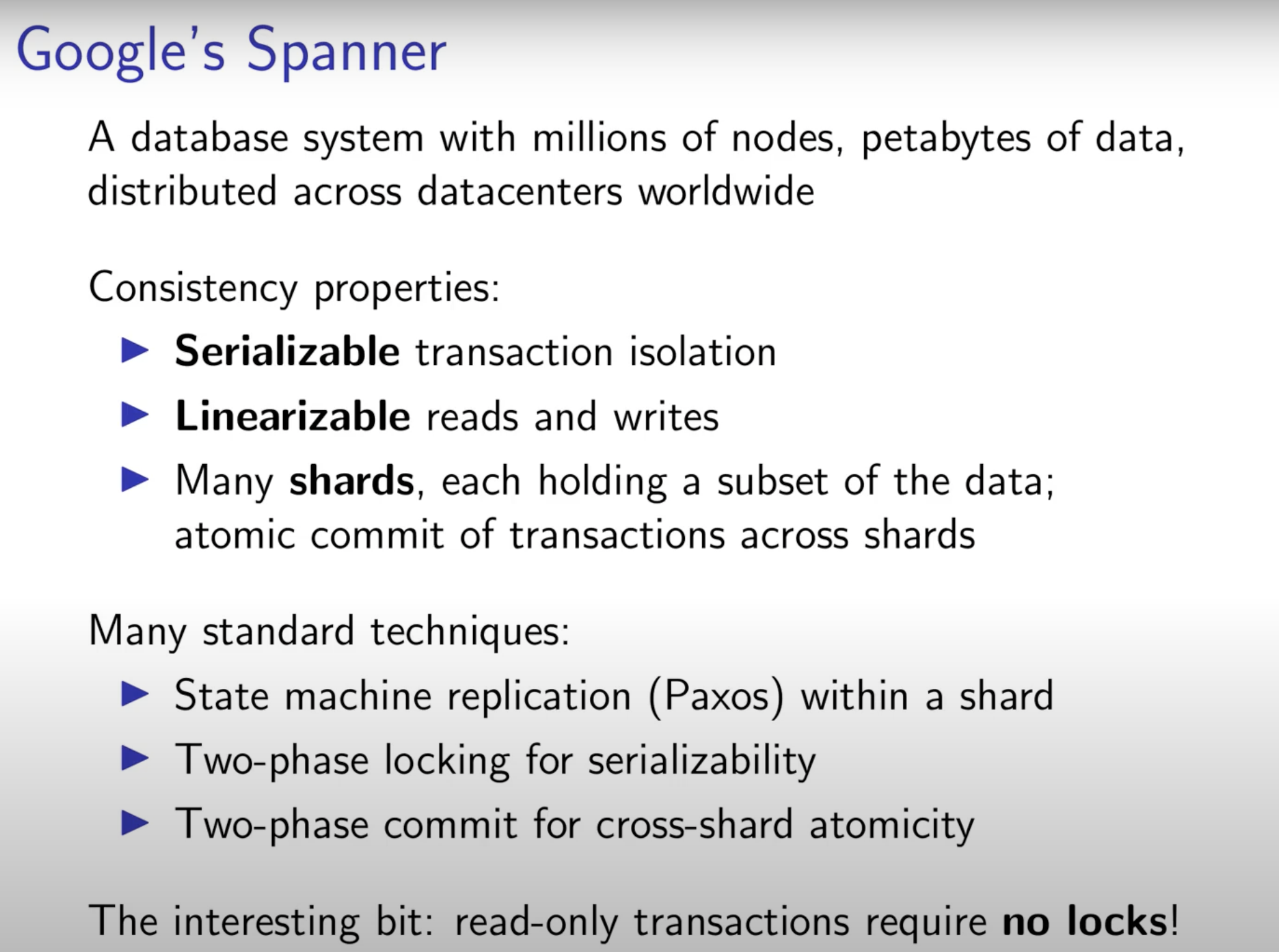
MVCC: no locking consistent read, with snapshot. (with no write after read casual consistency problem)
read transcation(Tr) can only read transcations before Tr;
Write transcation(Tw) will not overwrite value, but create a new value with timestamp.
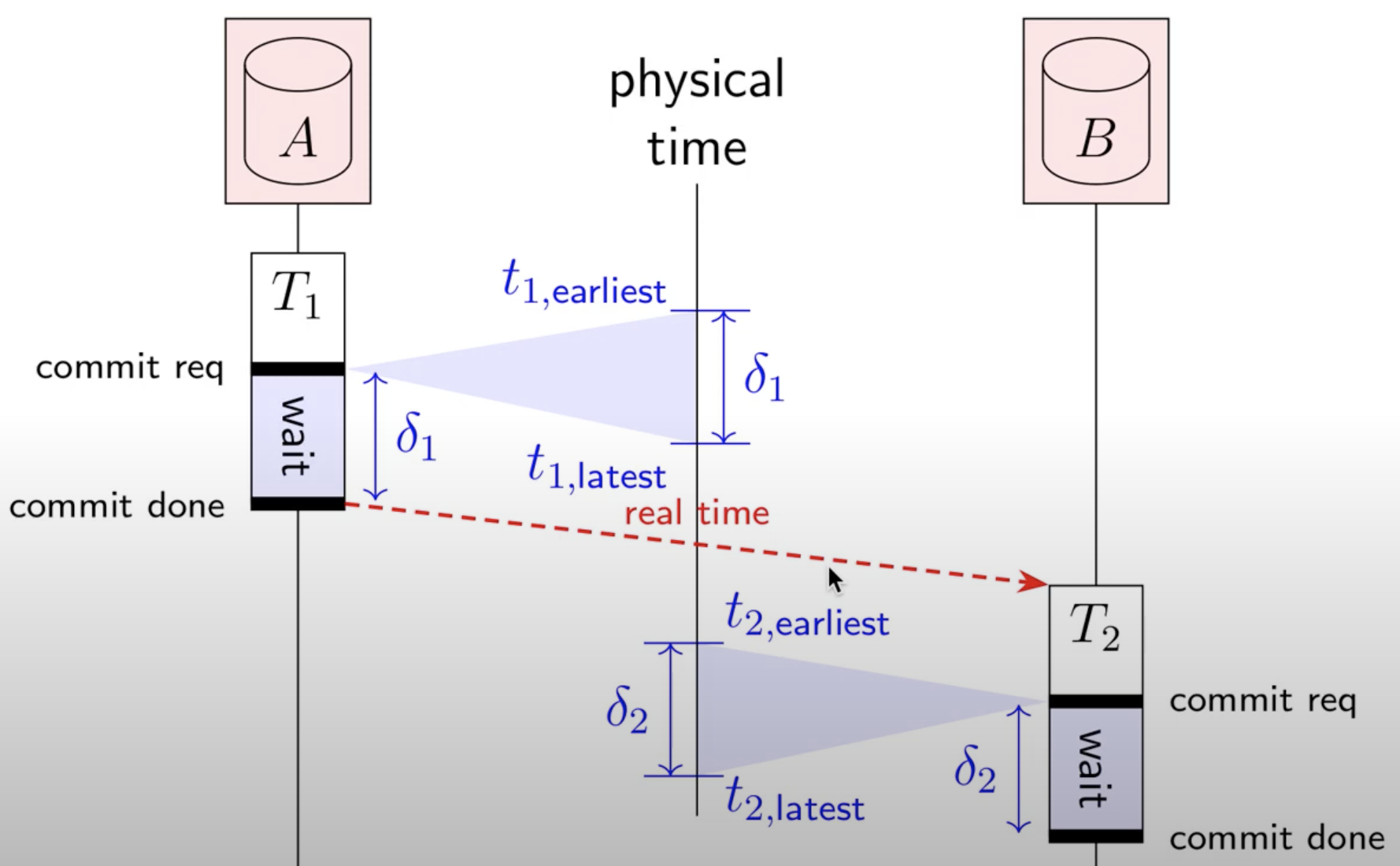
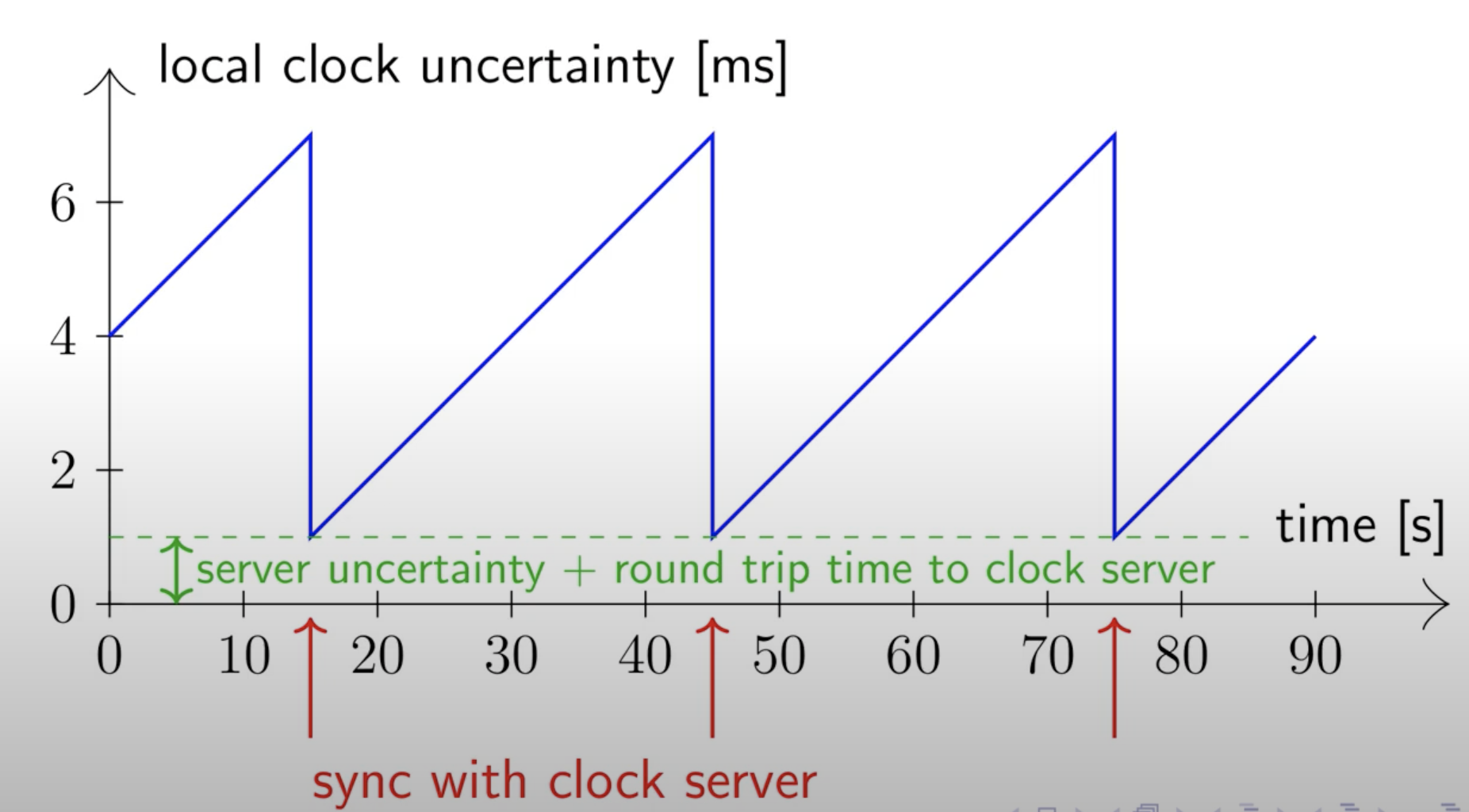
MySQL local timestamp, Spanner global unique timestamp generate.